Summary:
-
- Rhodamine B Ban: Several state government bans Rhodamine B in food due to health risks.
-
- What is Rhodamine B?: A chemical used in dyes and sometimes food, linked to potential health hazards.
-
- FSSAI Regulations: Lists permitted synthetic colouring agents, excluding Rhodamine B.
What is the news?
-
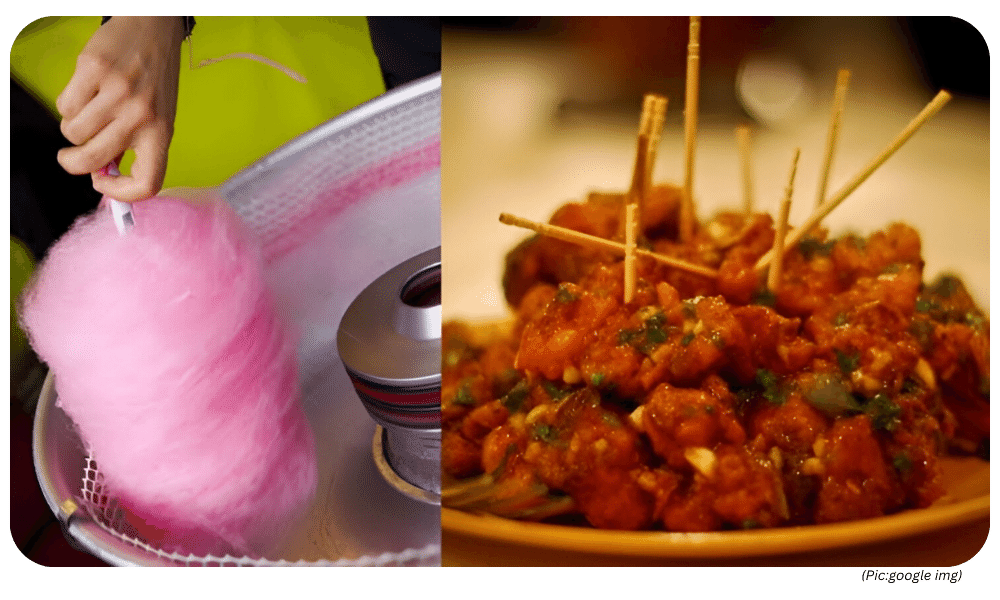
- Several Indian state governments have taken a commendable step by banning the use of artificial colours, particularly Rhodamine B, in popular street foods like gobi manchurian and cotton candy.
-
- This decision prioritizes public health, especially of children, who are more susceptible to the harmful effects of these synthetic dyes.
The Health Concerns:
-
- Rhodamine B is a synthetic colour widely used in industries, but its presence in food raises serious concerns. Studies suggest potential links between its consumption and adverse health effects like hyperactivity in children, and even cancer in some cases. While the long-term consequences require further research, the potential risks are significant enough to warrant a precautionary approach.
Beyond the Colourful Facade:
-
- The vibrant colours of street food often mask the use of harmful additives. This ban highlights the need for stricter regulations on food safety and transparency in ingredients. Consumers deserve to know what they are eating, and such bans encourage responsible practices within the food industry.
A Call for Alternatives:
-
- The ban presents an opportunity to explore safer alternatives. Natural colours derived from fruits and vegetables can effectively enhance the visual appeal of food without compromising health. This shift can encourage innovation and promote healthier choices for both consumers and food vendors.
Enforcement and Awareness:
-
- The success of this ban hinges on effective enforcement mechanisms. Regular food safety inspections and stringent penalties for non-compliance are crucial. Additionally, public awareness campaigns can educate consumers about the risks of artificial colours and encourage them to make informed choices.
A Nationwide Step?
-
- The initiative by these state governments sets a positive precedent. A nationwide ban on harmful artificial colours in food products would ensure consistent application and provide broader protection for public health. This, coupled with stricter regulations and a focus on natural alternatives, can create a safer and healthier food environment for all.
Conclusion:
-
- The ban on harmful colours in popular street food is a welcome step towards prioritizing public health. It emphasizes the need for stricter regulations, exploration of safer alternatives, and increased awareness. By adopting these measures, we can ensure that the vibrant colours of our food don’t come at the cost of our well-being.
What is Rhodamine B?
Rhodamine B is a chemical compound that falls into two main categories:
-
- Dye: It’s a widely used synthetic dye, known for its bright red or violet color.
- Fluorescent tracer: In other applications, it functions as a fluorescent tracer. This means it absorbs light at a specific wavelength and emits light at a different wavelength, making it easily detectable with instruments called fluorometers.
Here’s a breakdown of its key characteristics:
-
- Chemical Formula: C28H31ClN2O3
- Appearance: Red to violet powder
Applications:
-
- Dyes: Commonly used in textiles, leather, paper printing, paints, and even colored glass and plastics industries.
- Food Industry (controversial): Despite its dyeing properties, some street food vendors use Rhodamine B to achieve a vibrant red color in dishes like gobi manchurian (cauliflower dish). However, due to potential health concerns, its use in food is being banned in several Indian states.
- Fluorescent Tracer: Used in scientific research and various industrial applications to trace the movement of fluids or materials.
Health Concerns:
While research is ongoing, some studies suggest potential links between consuming Rhodamine B and adverse health effects, particularly in children. These include:
-
- Hyperactivity
- In some cases, even cancer (although long-term effects require further investigation)
- Due to these potential risks, a precautionary approach is being taken, leading to bans on its use in food items.
Why Rhodamine B is banned?
-
- Rhodamine B is banned in food items in several Indian states due to potential health concerns, particularly for children. While the long-term effects require further research, here’s a breakdown of the key reasons for the ban:
Potential Health Risks:
- Studies suggest links between consuming Rhodamine B and adverse health effects, including:
-
- Hyperactivity: This is a major concern, as children are more susceptible to the effects of this dye.
- Potential Cancer Risk: Some studies suggest a possible link to cancer in some cases, although more research is needed to confirm this.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: The long-term consequences of consuming Rhodamine B are not fully understood, making a precautionary approach necessary.
Unintended Consequences:
-
- Food Safety Concern: Rhodamine B is an industrial dye, not intended for food consumption. Its presence in food indicates a disregard for food safety regulations.
- Public Health Risk: As a synthetic dye, it may have unintended consequences when ingested, potentially causing allergic reactions or other health problems in some individuals.
Alternative Availability:
-
- Safer Alternatives Exist: Natural colours derived from fruits and vegetables can effectively replace synthetic dyes like Rhodamine B. These pose a much lower health risk and offer vibrant colours.
- Promoting Responsible Practices: The ban encourages food vendors to utilize safer alternatives and prioritize the health of their customers.
Overall, the ban on Rhodamine B prioritizes public health by:
-
- Reducing the risk of potential health problems associated with this dye.
- Promoting safer practices in the food industry.
- Encouraging the use of natural and healthier alternatives.
While further research may be needed to definitively establish the long-term effects of Rhodamine B, the potential health concerns and availability of safer alternatives justify this precautionary measure.
QuizTime:
Mains Questions:

Question 1:
Several Indian states have banned the use of artificial colours, particularly Rhodamine B, in popular street foods. Critically examine the public health rationale behind this ban. Suggest measures to ensure the effectiveness of such bans. (250 words)
Model Answer:
The ban on artificial colours like Rhodamine B is a necessary step to safeguard public health, particularly for children. Here’s why:
-
- Potential Health Risks: Studies suggest links between consuming Rhodamine B and hyperactivity, and even potential cancer risks. The unknown long-term effects necessitate a precautionary approach.
- Food Safety Concerns: Rhodamine B is an industrial dye, not intended for food consumption. Its presence indicates a disregard for food safety regulations.
To ensure the effectiveness of such bans:
-
- Strict Enforcement: Regular food safety inspections with stringent penalties for non-compliance are crucial.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educate consumers about the risks of artificial colours and empower them to make informed choices.
- Focus on Alternatives: Promote the use of natural colours derived from fruits and vegetables as safe and vibrant alternatives.
Question 2:
The editorial mentions a shift towards natural colours in food products. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using natural colours compared to artificial colours in the food industry. (250 words)
Model Answer:
Advantages of Natural Colours:
-
- Healthier Option: Natural colours pose a lower health risk compared to synthetic dyes like Rhodamine B.
- Consumer Preference: Consumers increasingly seek natural and organic ingredients, making natural colours a market advantage.
- Sustainability: Natural colours can be derived from renewable sources, promoting environmental sustainability.
Disadvantages of Natural Colours:
-
- Colour Consistency: Natural colours may exhibit slight variations in shade compared to the uniformity of artificial dyes.
- Light Sensitivity: Some natural colours may fade or lose vibrancy when exposed to light or heat, requiring adjustments in storage and preparation.
- Cost: Natural colours can sometimes be more expensive to produce compared to synthetic alternatives.
Despite these disadvantages, the health benefits and growing consumer demand make natural colours a viable and preferable option for the food industry.
Remember, these are just two examples of UPSC Mains questions inspired by the current affairs. Feel free to modify and adapt them further to fit your specific needs and writing style. Good luck with your preparation!
Relevance to the UPSC Prelims and Mains syllabus under the following topics:

Prelims:
-
- General Studies Paper I: UPSC Current Affairs
Mains:
-
- General Studies Paper II (GS Paper II): Governance, Constitution, Polity and Social Justice – You can discuss this ban in the context of issues related to food safety and public health. Analyze the role of the government in regulating food additives and ensuring consumer protection.
- General Studies Paper III (GS Paper III): Technology, Economic Development, Security and Social Change – Briefly mention this ban as an example of a policy initiative aimed at promoting public health and responsible practices in the food industry. You can discuss the potential economic implications for street vendors who may need to adapt their practices.










0 Comments