Summary:
-
- Shrinkflation in FMCG: The article discusses the issue of shrinkflation in the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry, where companies reduce product quantity while keeping prices the same.
-
- Consumer Impact: Shrinkflation affects consumers by eroding their purchasing power and trust, as they get less for the same price.
-
- Causes: The resurgence of shrinkflation is attributed to rising input costs, global supply chain disruptions, inflationary pressures, and consumer price sensitivity.
-
- Solutions: To combat shrinkflation, the article suggests consumer awareness, regulatory transparency, alternative packaging, and a focus on innovation.
What is the news?
-
- Shrinkflation is again became a topic of concern within the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry.
Shrinkflation: A Looming Shadow Over Consumer Goods
-
- Shrinkflation, the deceptive practice of reducing product quantity while maintaining the price, has re-emerged as a major concern within the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry. This editorial explores the reasons behind this trend, its impact on consumers, and potential solutions to ensure fair market practices.
Understanding Shrinkflation:
-
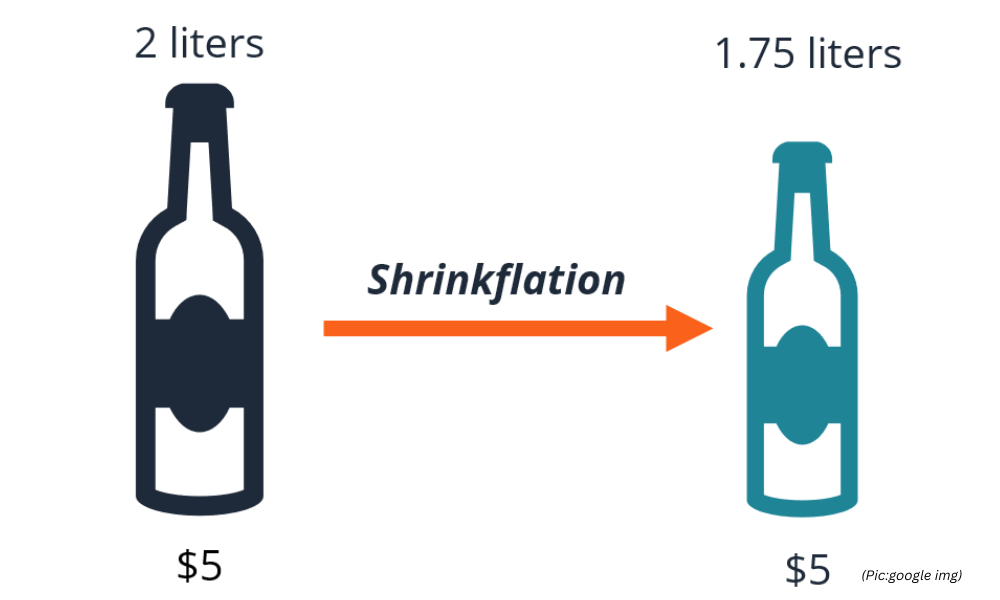
- In a scenario of rising input costs, particularly raw materials like crude oil, palm oil, and packaging materials, FMCG companies face pressure on their profit margins. Shrinkflation allows them to maintain their pricing structure while subtly reducing the quantity consumers receive. For example, a 2 liters juice bottle might shrink to 1.75 liters juice bottle, or a 1-liter bottle of juice might become 950 mililiters, all while retaining the original price tag.
Impact on Consumers:
-
- Shrinkflation erodes purchasing power and deceives consumers. They essentially pay the same for less, impacting their ability to manage household budgets and maintain their standard of living. This is particularly concerning for low-income families who rely on these essential goods. Furthermore, shrinkflation undermines consumer trust in brands and creates a sense of being misled.
Reasons for Resurgence:
The recent resurgence of shrinkflation can be attributed to several factors:
-
- Global Supply Chain Disruptions: The ongoing pandemic and geopolitical tensions have disrupted global supply chains, leading to fluctuations in raw material prices and shortages. This puts pressure on FMCG companies’ production costs.
-
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising inflation across the board, including energy and transportation costs, further squeezes profit margins for FMCG companies.
-
- Consumer Price Sensitivity: Companies are cautious about blatantly raising prices, fearing a decline in demand. Shrinkflation allows them to maintain a price point they believe consumers are willing to pay.
Seeking Solutions:
Combatting shrinkflation requires a multi-pronged approach:
-
- Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about shrinkflation tactics empowers them to make informed choices. Consumers can compare unit prices (price per gram/liter) to identify better value options.
-
- Regulation and Transparency: Regulatory bodies can play a role by requiring manufacturers to clearly display product weight or volume on packaging, making it easier for consumers to compare quantities.
-
- Alternative Packaging: FMCG companies can explore alternative packaging materials or sizes that offer cost savings without compromising on product quantity.
-
- Focus on Innovation: Companies should prioritize innovation to improve production efficiency and explore ways to reduce waste throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion:
-
- Shrinkflation is a deceptive practice that erodes consumer trust and purchasing power. By promoting transparency, encouraging informed consumer choices, and exploring alternative solutions, stakeholders can work together to ensure fair market practices and protect consumer interests in the FMCG sector. Ultimately, a balance needs to be struck between maintaining affordability and ensuring consumers receive the value they expect from the products they purchase.
QuizTime:
Mains Questions:

Question 1:
Shrinkflation, the practice of reducing product quantity while maintaining price, has re-emerged as a concern in the FMCG sector. Analyze the factors driving this trend and its impact on consumers and the market. Suggest measures to promote fair practices and consumer protection in this context.(250 words)
Model Answer:
Factors Driving Shrinkflation:
-
- Rising Input Costs: Escalating prices of raw materials like crude oil, palm oil, and packaging materials squeeze profit margins for FMCG companies.
- Inflationary Pressures: Overall inflation, including energy and transportation costs, further increases production costs.
- Consumer Price Sensitivity: Companies hesitate to raise prices openly due to the fear of declining demand. Shrinkflation allows them to maintain a price point perceived as acceptable by consumers.
Impact of Shrinkflation:
-
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Consumers get less for the same price, impacting their ability to manage household budgets and maintain their standard of living.
- Erosion of Trust: Deceptive practices like shrinkflation undermine consumer trust in brands and create a sense of being misled.
- Market Distortion: Shrinkflation can distort fair competition as companies prioritize maintaining price points over product innovation.
Promoting Fair Practices and Consumer Protection:
-
- Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about shrinkflation tactics empowers them to make informed choices. Comparing unit prices (price per gram/liter) helps identify better value options.
- Regulation and Transparency: Regulatory bodies can mandate clear display of product weight or volume on packaging, allowing for easy comparison of quantities.
- Alternative Packaging: Companies should explore alternative, cost-effective packaging materials or sizes that maintain product integrity without compromising quantity.
- Focus on Innovation: Investing in production process optimization and exploring ways to reduce waste throughout the supply chain can help companies manage costs and avoid shrinkflation.
Question 2:
The recent resurgence of shrinkflation in the FMCG industry highlights the need for a balanced approach to managing costs and protecting consumer interests. Discuss the role of various stakeholders, including companies, regulatory bodies, and consumer organizations, in ensuring fair market practices in the FMCG sector.(250 words)
Model Answer:
Roles of Stakeholders:
Companies:
-
- Upholding ethical practices by prioritizing product quality and quantity over deceptive tactics like shrinkflation.
- Promoting transparency through clear labeling and communication of product changes.
- Investing in innovation and exploring cost-saving measures throughout the production chain.
Regulatory Bodies:
-
- Developing and enforcing regulations for fair labeling practices that display accurate product information.
- Monitoring market trends and taking action against companies resorting to deceptive practices.
- Encouraging self-regulation within the FMCG industry through industry guidelines.
Consumer Organizations:
-
- Educating consumers about shrinkflation tactics and fostering awareness of unit pricing strategies.
- Representing consumer interests and advocating for fair pricing practices through petitions and legal action.
- Collaborating with regulatory bodies to develop and implement consumer-protection policies.
A collaborative effort by all stakeholders – companies, regulators, and consumer organizations – is crucial to ensure fair market practices, protect consumer interests, and promote transparency in the FMCG sector. By upholding ethical practices, promoting innovation, and prioritizing consumer trust, stakeholders can create a sustainable and responsible environment for FMCG businesses.
Remember: These are just sample answers. It’s important to further research and refine your responses based on your own understanding and perspective. Read entire UPSC Current Affairs.
Relevance to the UPSC Prelims and Mains syllabus under the following topics:

Prelims:
-
- GS Paper I: Economy:While not a specific question on shrinkflation, the Prelims could ask about government initiatives or policies related to inflation control or consumer protection. Understanding the concept of shrinkflation and its impact on purchasing power might be helpful in answering such questions.
Mains:
-
- GS Paper III – Indian Economy: This paper could have questions on consumer protection, the role of competition in the market, or challenges faced by the FMCG sector. Analyzing shrinkflation through these lenses can demonstrate your understanding of market dynamics.
- GS Paper IV – Ethics, Integrity, and Aptitudes: This paper might have a case study-based question on a company resorting to shrinkflation. You could analyze this ethically, considering its impact on consumers, transparency, and responsible business practices.











0 Comments